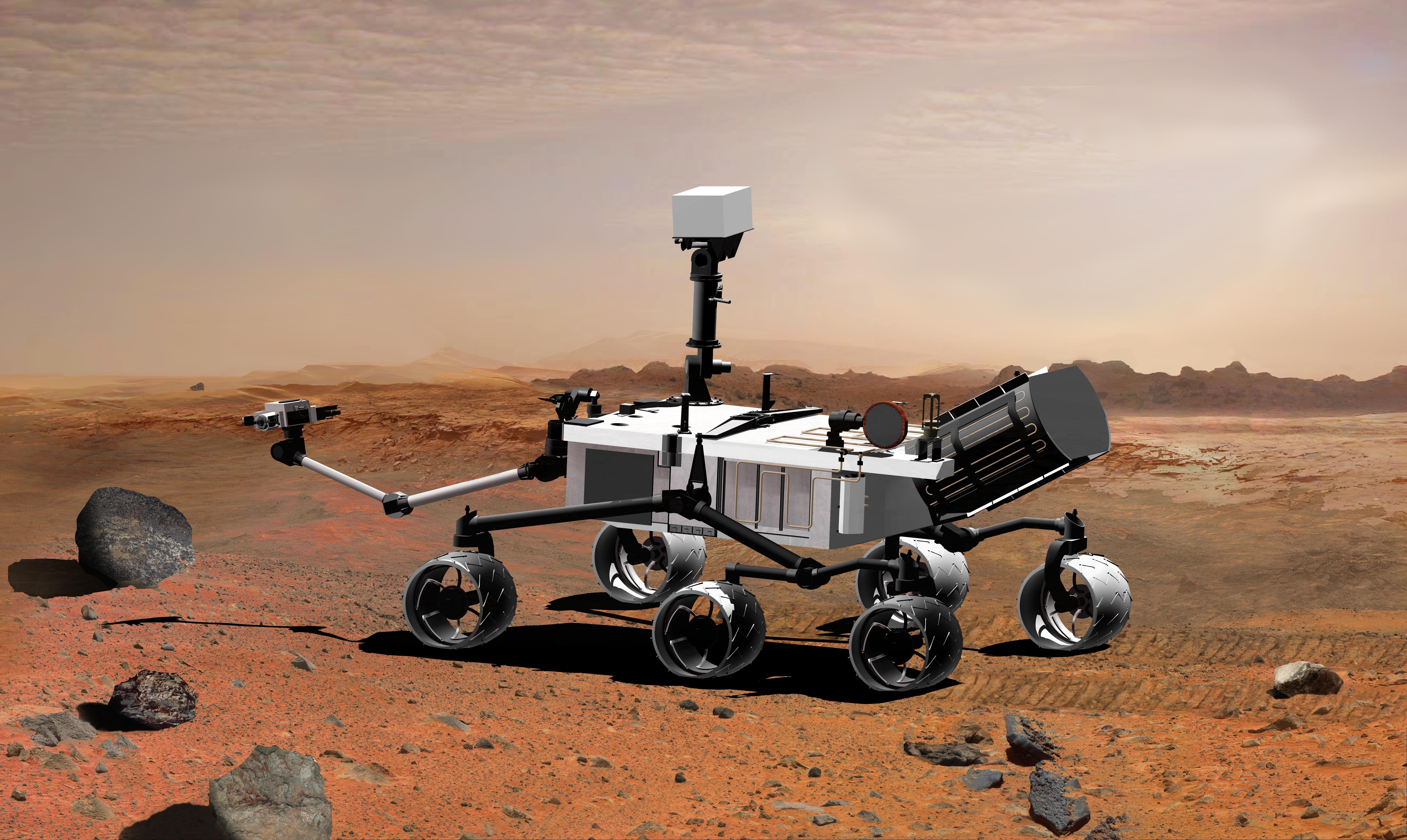
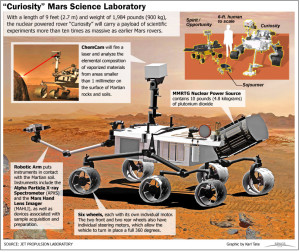
The Mars Science Laboratory and its rover centerpiece, Curiosity, is the most ambitious Mars mission yet flown by NASA. The rover’s primary mission is to find out if Mars is, or was, suitable for life. Another objective is to learn more about the red planet’s environment.
Curiosity’s size allows it to carry a host of scientific experiments to zap, analyze and take pictures of any rock within reach of its 7-foot (2 meters) arm. Curiosity is about the size of a small SUV. It is 9 feet 10 inches long by 9 feet 1 inch wide (3 m by 2.8 m) and about 7 feet high (2.1 m). It weighs 2,000 pounds (900 kilograms). Curiosity’s wheels have a 20-inch (50.8 cm) diameter.
Engineers at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory designed the rover to roll over obstacles up to 25 inches (65 centimeters) high and to travel about 660 feet (200 meters) per day. The rover’s power comes from a multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator, which produces electricity from the heat of plutonium-238’s radioactive decay.