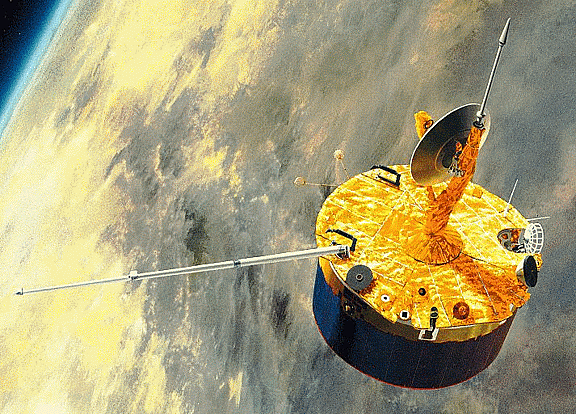
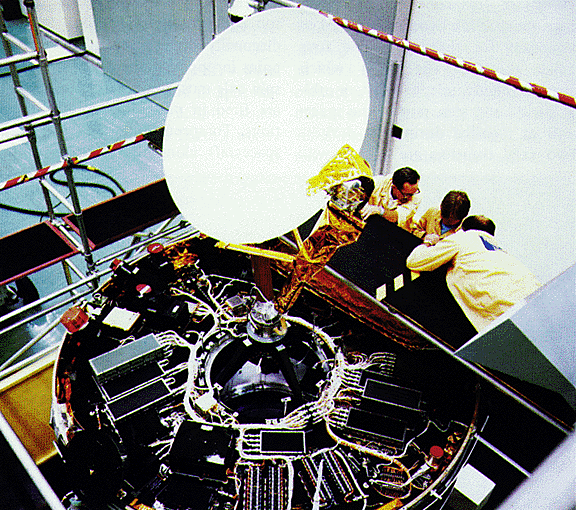
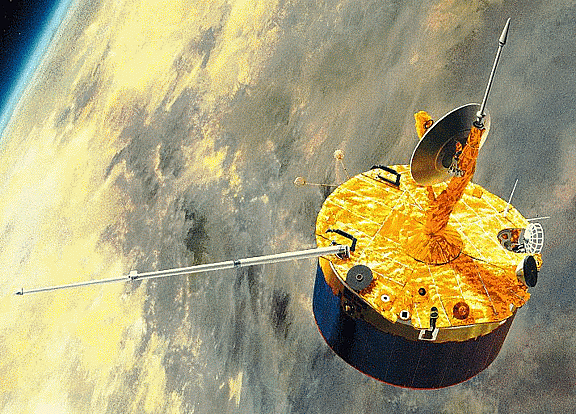
When the Pioneer Venus Orbiter launched 38 years ago today, it was only intended to operate for one Venusian year. As it turns out, most of its instruments operated for more than 13 years.
The purpose of this spacecraft was to investigate the atmosphere of Venus.
Launched on May 20th, 1978, the orbiter taught us many things about Venus. It measured the structure of the upper atmosphere and ionosphere. It investigated how the solar wind interacts with the ionosphere and magnetic field around Venus.
Additionally, atmosphere and surface characteristics were determined. The orbiter created the first radar topographic map of the surface of Venus’s. The orbiter was even able to measure cosmic gamma-ray bursts while in Venus orbit.
The instruments onboard were designed to measure vertical cloud distribution, infrared (IR) emissions from the atmosphere, and scattered and emitted UV light, among other measurements.
The orbiter began the last phase of the mission in May 1992. It eventually ran out of fuel and was destroyed while entering the atmosphere.
Learn more about this important piece of space history at NASA.gov.